Decoding Obesity: Understanding Causes and Prevention, 99 Causes of Obesity, BMI
What is Obesity?
Obesity is a medical condition characterized by the accumulation of excess body fat, leading to adverse effects on health. It is usually determined by the Body Mass Index (BMI), where a BMI of 30 or higher is considered obese.
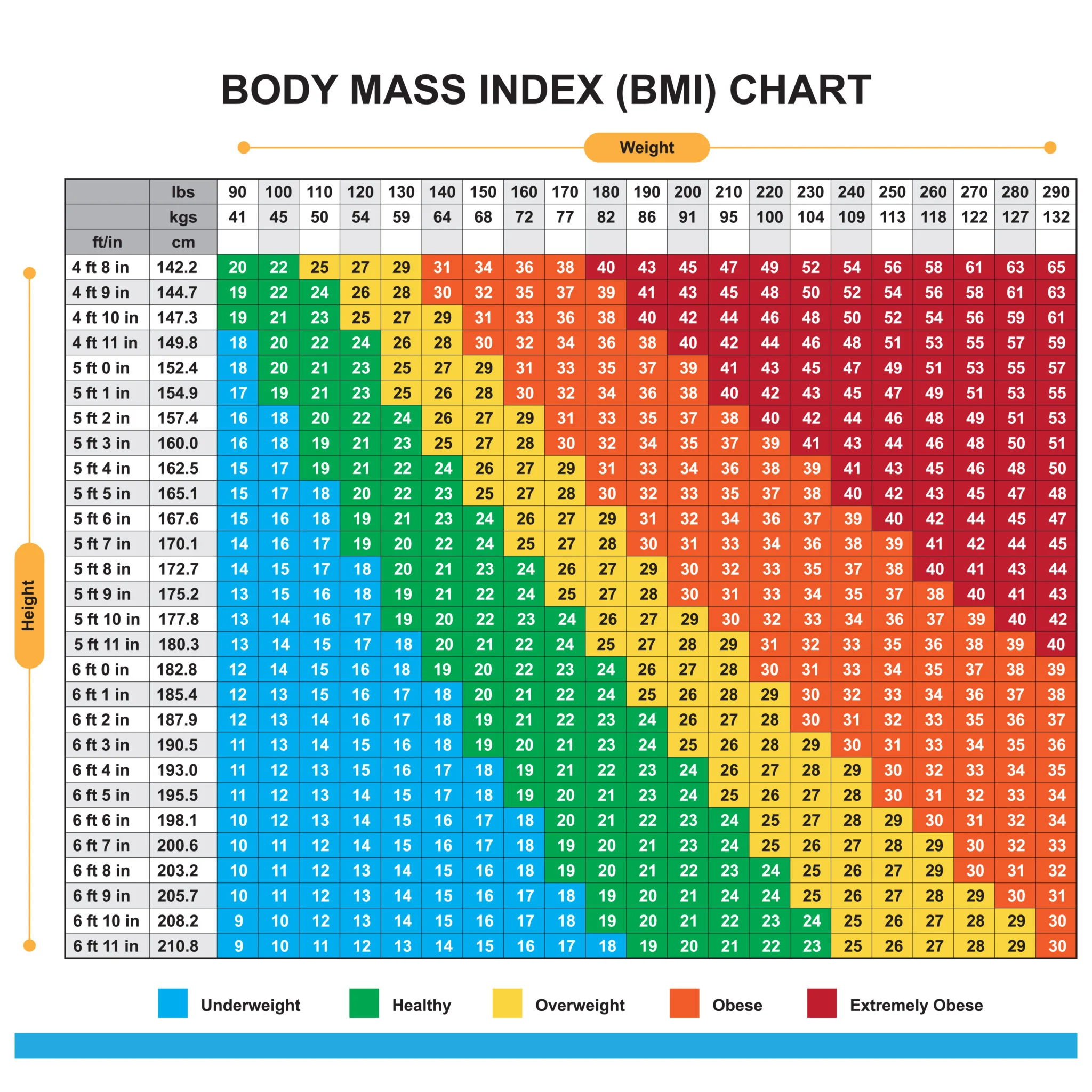
Understanding BMI (Body Mass Index) and Weight
What is BMI?
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a numerical measurement derived from an individual’s height and weight. It provides a general indication of body fatness and helps categorize individuals into different weight status classifications.

BMI Calculation Formula:
BMI is calculated using the following formula:
[ BMI = \frac{weight (kg)}{height (m)^2} ]
BMI Categories:
- Underweight: BMI less than 18.5
- Normal Weight: BMI between 18.5 and 24.9
- Overweight: BMI between 25 and 29.9
- Obesity – Class 1: BMI between 30 and 34.9
- Obesity – Class 2: BMI between 35 and 39.9
- Obesity – Class 3: BMI 40 or greater (commonly referred to as morbid obesity)
Interpreting BMI:

Underweight:
- Implications: This may indicate nutritional deficiencies or other health concerns.
- Considerations: Consultation with a healthcare professional is recommended for assessment and guidance.
Normal Weight:
- Implications: Generally considered a healthy weight range for most individuals.
- Considerations: Maintaining a balanced diet and regular exercise supports overall well-being.
Overweight:
- Implications: Increased risk of certain health issues like heart disease and diabetes.
- Considerations: Adopting healthier lifestyle choices, including diet and exercise, is encouraged.
Obesity – Class 1:
- Implications: Moderate risk of obesity-related health conditions.
- Considerations: Lifestyle modifications, including dietary changes and increased physical activity, are recommended.
Obesity – Class 2:
- Implications: High risk of obesity-related health conditions.
- Considerations: Medical supervision and comprehensive lifestyle changes may be necessary.
Obesity – Class 3 (Morbid Obesity):
- Implications: Severe risk of obesity-related health issues and complications.
- Considerations: Medical intervention, including surgery, may be considered under professional guidance.
Limitations of BMI:
- Muscle Mass: BMI does not differentiate between muscle and fat. Athletes or individuals with high muscle mass may have a higher BMI without excess body fat.
- Body Composition: It does not consider the distribution of fat, which is crucial for assessing health risks.
- Age and Gender: BMI standards may vary with age and gender.
Weight Management:
- Healthy Weight Loss: Aim for a gradual and sustainable loss of 1-2 pounds per week.
- Weight Gain: Seek professional advice for a healthy approach, especially for underweight individuals.
- Maintaining a Healthy BMI: Focus on balanced nutrition, regular physical activity, and overall well-being.
Consulting a Healthcare Professional:
It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice, as BMI is a screening tool and not a definitive health assessment. Factors such as medical history, body composition, and individual health goals should be considered for a comprehensive approach to well-being.
Remember, maintaining a healthy weight is just one aspect of overall health, and individual well-being involves various factors beyond BMI.

99 Causes of Obesity: Unveiling the Multifaceted Influences
Understanding obesity involves recognizing various contributing factors. While it’s challenging to list all potential causes, here are 99 diverse influences:
Genetic Factors:
- 1. Genetic predisposition
- 2. Family history of obesity
- 3. Inherited metabolism issues
Lifestyle Choices:
- 4. Unhealthy dietary habits
- 5. Lack of physical activity
- 6. Sedentary lifestyle
- 7. Overconsumption of processed foods
- 8. High-calorie beverages
Environmental Influences:
- 9. Access to unhealthy food options
- 10. Food marketing practices
- 11. Socioeconomic factors
- 12. Urban environments with limited green spaces
- 13. Exposure to endocrine-disrupting pollutants
Medical Conditions:
- 14. Hypothyroidism
- 15. Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- 16. Cushing’s syndrome
- 17. Insulin resistance
- 18. Prader-Willi syndrome
Medications:
- 19. Antidepressants
- 20. Corticosteroids
- 21. Antipsychotic medications
- 22. Certain contraceptives
Psychological Factors:
- 23. Emotional eating
- 24. Stress-related overeating
- 25. Depression
- 26. Anxiety disorders
Sleep Patterns:
- 27. Sleep deprivation
- 28. Sleep apnea
- 29. Disrupted circadian rhythms
Social Factors:
- 30. Peer influences
- 31. Cultural norms
- 32. Lack of social support
- 33. Childhood trauma
Physiological Factors:
- 34. Metabolic rate variations
- 35. Leptin resistance
- 36. Ghrelin imbalances
- 37. Insulin resistance
Pregnancy-Related Factors:
- 38. Gestational diabetes
- 39. Excessive gestational weight gain
- 40. Postpartum weight retention
Age-Related Influences:
- 41. Aging metabolism
- 42. Hormonal changes during menopause
Dietary Factors:
- 43. High intake of sugary foods
- 44. Excessive consumption of high-fat foods
- 45. Low fiber intake
- 46. Large portion sizes
Cultural Practices:
- 47. Celebratory feasting
- 48. Social expectations around food
Addiction and Dependencies:
- 49. Food addiction
- 50. Substance abuse issues
Genetic Syndromes:
- 51. Down syndrome
- 52. Turner syndrome
- 53. Alström syndrome
Digestive Disorders:
- 54. Hypothalamic injury
- 55. Prader-Willi-like syndrome
- 56. Hypothalamic injury
Hormonal Imbalances:
- 57. Growth hormone deficiency
- 58. Hyperinsulinemia
- 59. Hypercortisolism
Neurological Factors:
- 60. Brain injuries affecting the hypothalamus
- 61. Neurological disorders impacting appetite control
Childhood Influences:
- 62. Early feeding practices
- 63. Lack of breastfeeding
- 64. Childhood trauma affecting eating behaviors
Food Addiction:
- 65. Binge eating disorder
- 66. Emotional eating
- 67. Reward-based eating
Social Inequality:
- 68. Limited access to nutritious food
- 69. Disparities in healthcare access
Unhealthy School Environments:
- 70. Lack of physical education
- 71. Availability of unhealthy cafeteria options
Medical Treatments:
- 72. Corticosteroid therapy
- 73. Antipsychotic medications
- 74. Chemotherapy
Gut Microbiota:
- 75. Imbalances in gut bacteria
- 76. Microbiome variations affecting metabolism
Dietary Additives:
- 77. Artificial sweeteners
- 78. High-fructose corn syrup
Dental Health:
- 79. Oral health impacting diet choices
Emotional Trauma:
- 80. Emotional and physical abuse
- 81. Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
Hormonal Birth Control:
- 82. Impact on weight regulation
Hypertension Medications:
- 83. Certain antihypertensive drugs
Insufficient Physical Activity:
- 84. Sedentary jobs
- 85. Lack of recreational exercise
Low Socioeconomic Status:
- 86. Limited access to fresh produce
- 87. Reduced opportunities for physical activity
Neighborhood Environment:
- 88. Lack of safe spaces for outdoor activities
- 89. Limited access to gyms and parks
Economic Factors:
- 90. Food affordability
- 91. Cost of healthy food options
Cultural Perception:
- 92. Stigmatization of Obesity
- 93. Societal pressure on body image
Food Deserts:
- 94. Limited access to grocery stores with fresh produce
Food Industry Practices:
- 95. Marketing of unhealthy foods
- 96. Proliferation of fast-food chains
Dietary Misinformation:
- 97. Lack of nutritional education
- 98. Misleading dietary advice
- 99. Diet fads and trends

Prevention of Obesity: Empowering Healthy Lifestyles
1. Balanced Nutrition:
Ensure a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.

2. Regular Physical Activity:
Incorporate regular exercise into daily routines.

3. Adequate Sleep:
Prioritize healthy sleep patterns to support metabolic balance.
4. Stress Management:
Develop effective stress coping mechanisms.
5. Behavioral Counseling:
Seek professional guidance for behavior modification.
6. Medical Supervision:
Regular health check-ups to monitor weight-related health factors.
7. Community Engagement:
Promote community initiatives supporting healthy living.
8. Education and Awareness:
Increase awareness about the causes and consequences of obesity.
9. Policy Changes:
Advocate for policies promoting access to healthy foods and environments.
10. Individual Empowerment:
Take proactive steps towards a healthier lifestyle.
Understanding the multifaceted nature of obesity allows individuals and communities to address its root causes and work collectively toward prevention.






